What Causes Tooth Sensitivity After Whitening
Tooth sensitivity after whitening is a common yet temporary side effect for many people. The primary reason for this sensitivity is the active ingredients in whitening products, typically hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These chemicals penetrate the enamel, the outer layer of your teeth, to break down stain molecules. During this process, the chemicals can also irritate the nerves inside the teeth, leading to the sensation of sensitivity. This is more likely to occur if you already have sensitive teeth or if the whitening product is used more frequently or in higher concentrations than recommended. Understanding the underlying causes is the first step in effectively managing and alleviating the discomfort associated with tooth sensitivity after whitening. It is important to note that the intensity of sensitivity can vary widely, with some individuals experiencing only mild discomfort while others may feel significant pain. This depends on various factors including the individual’s oral health, the type of whitening treatment used, and the concentration of the bleaching agent.
Why Does Whitening Cause Sensitivity
The process of teeth whitening itself is inherently linked to the potential for increased tooth sensitivity. As the whitening agents, such as hydrogen peroxide, work to break down stains, they can also affect the enamel and the underlying dentin of your teeth. The enamel is the outermost protective layer, and although it’s incredibly strong, it can become slightly more porous during the whitening process. This increased porosity allows the whitening agents to reach the nerves within the teeth more easily, leading to temporary sensitivity. Moreover, the dentin, which contains tiny tubules that lead to the nerves, becomes more exposed as the enamel is affected, thus increasing sensitivity. This is also why individuals with pre-existing conditions like enamel erosion or receding gums are more likely to experience sensitivity. The concentration of the whitening agent also plays a crucial role; higher concentrations often lead to more dramatic results, but they also increase the likelihood and intensity of sensitivity. Finally, the length of time the whitening agent is in contact with the teeth can impact the level of sensitivity experienced, highlighting the importance of following professional or product instructions carefully.
Hydrogen Peroxide Effect on Tooth Sensitivity
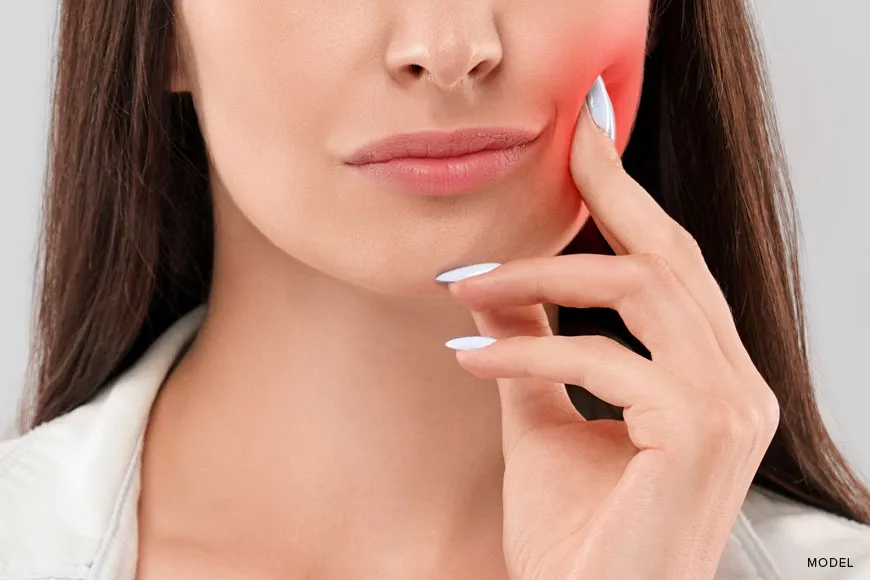

Hydrogen peroxide is the main active ingredient in most teeth whitening products, and it’s the primary culprit behind the temporary tooth sensitivity that many people experience. The way hydrogen peroxide works is by penetrating the enamel and breaking down the stain molecules that have discolored the teeth. This process, however, isn’t exclusive to stain removal; it also affects the structure of the enamel to some extent. As hydrogen peroxide works its magic, it can cause the enamel to become slightly dehydrated and more porous. This makes the tooth’s nerves more vulnerable to stimuli like hot or cold temperatures, leading to the sensation of sensitivity. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide in whitening products varies greatly, with professional treatments using higher concentrations than over-the-counter options. Higher concentrations typically lead to faster and more dramatic whitening results, but they also increase the potential for sensitivity. It is crucial to follow professional advice or product instructions regarding the duration and frequency of use to minimize potential discomfort.
Understanding Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is essentially a condition where your teeth become more sensitive to certain stimuli, such as hot or cold food and drinks, or even air. This heightened sensitivity occurs when the enamel, the protective outer layer of the tooth, is compromised, or when the gums recede, exposing the dentin underneath. Dentin contains tiny channels, called tubules, that lead directly to the nerves within the tooth. When these tubules are exposed, stimuli can more easily reach the nerves, causing pain or discomfort. The sensation can range from a mild twinge to a sharp, intense pain. Many factors can contribute to tooth sensitivity, including aggressive brushing, the use of abrasive toothpaste, acid erosion from certain foods or drinks, and, of course, teeth whitening. Understanding the root causes of your tooth sensitivity is important to choose the most effective management and treatment strategies. If your sensitivity is persistent or severe, it is important to consult a dentist to rule out any underlying dental issues and to get professional advice.
How to Treat Tooth Sensitivity After Whitening
Treating tooth sensitivity after whitening typically focuses on alleviating the discomfort and allowing the teeth to recover. The good news is that in most cases, this sensitivity is temporary, and there are several effective methods to manage it. One of the most common strategies is to use sensitive toothpaste. These toothpastes contain ingredients like potassium nitrate, which helps to block the nerve signals that cause sensitivity. Another effective approach is to avoid trigger foods and drinks like very hot or cold beverages, acidic foods, and sugary items. Maintaining a gentle brushing technique is essential to avoid further irritating the teeth and gums. Some individuals may also benefit from professional treatments, such as fluoride applications, provided by their dentist, which help to strengthen the enamel and reduce sensitivity. It is important to note that the best course of action will vary depending on the individual’s level of sensitivity and their specific dental situation.
Using Sensitive Toothpaste
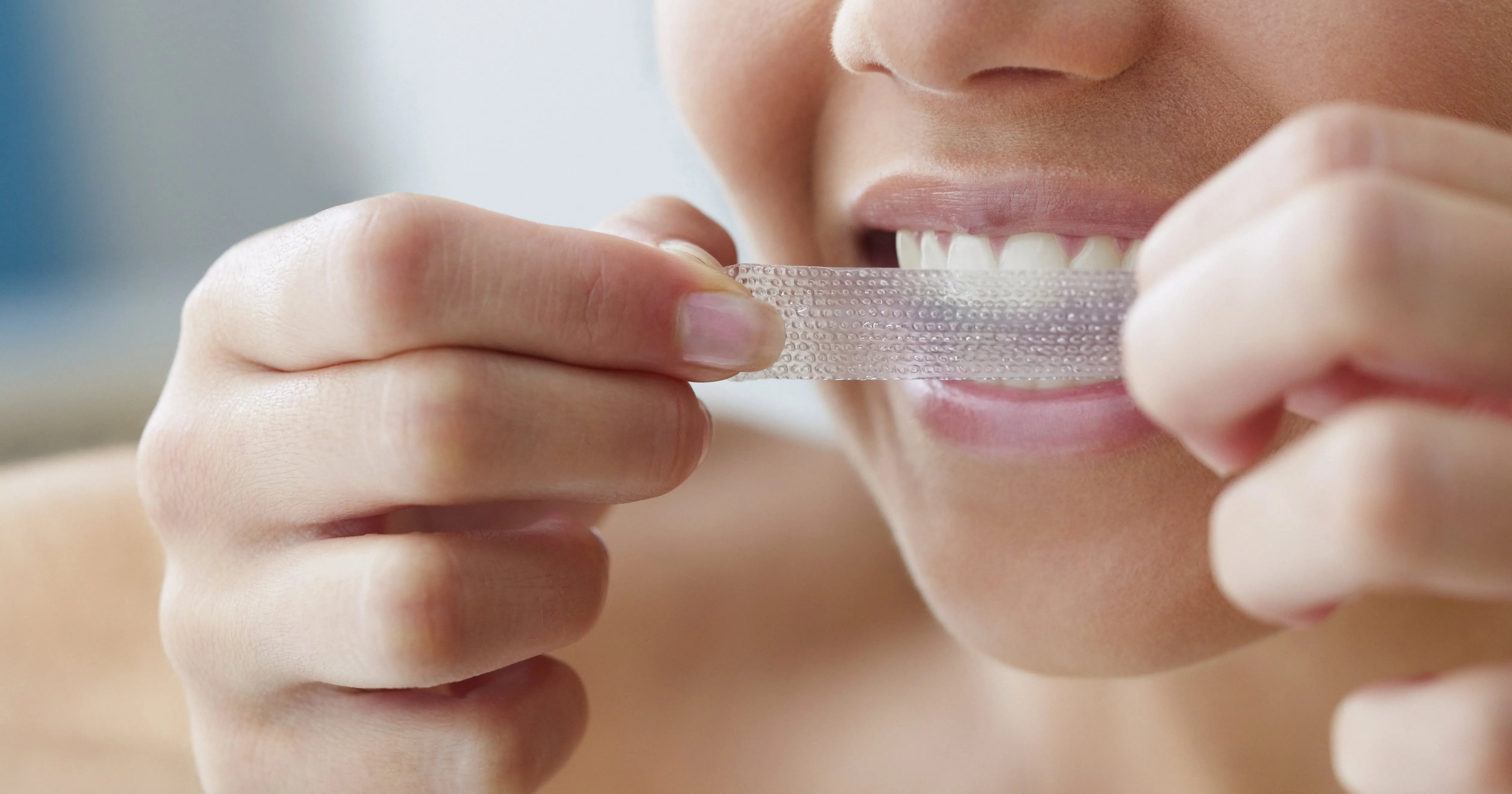

Using sensitive toothpaste is often the first line of defense against tooth sensitivity after whitening. These toothpastes are specially formulated to provide relief by blocking the pathways that transmit pain signals to your brain. They typically contain ingredients like potassium nitrate or stannous fluoride, which help to desensitize the nerves in your teeth. Potassium nitrate works by blocking the nerve endings, thereby reducing the sensation of pain. Stannous fluoride, on the other hand, helps to seal the dentin tubules, preventing irritants from reaching the nerves. It is important to use sensitive toothpaste regularly, as it may take several days or weeks before you experience noticeable relief. You should also make sure to use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid further irritating your teeth and gums. Moreover, be patient; consistent use of sensitive toothpaste is crucial for long-term management of tooth sensitivity. Consider consulting your dentist, they can recommend the most suitable sensitive toothpaste for your specific needs and dental condition.
Fluoride Treatment for Teeth
Fluoride treatments are a valuable tool for managing tooth sensitivity, including sensitivity that arises after teeth whitening. Fluoride helps to remineralize the enamel, making it stronger and less susceptible to external stimuli. It works by reinforcing the tooth’s structure and blocking the tiny tubules in the dentin, which can lead to sensitivity. Dentists often apply a concentrated fluoride treatment directly to the teeth in the form of a gel, varnish, or foam. This professional treatment delivers a higher dose of fluoride compared to what you might find in toothpaste or mouthwash. The application is usually quick and painless, and the benefits can last for several months. Following a fluoride treatment, it is usually recommended to avoid eating or drinking for a short period to allow the fluoride to fully absorb into the teeth. Regular fluoride treatments, as advised by your dentist, can be an effective way to reduce sensitivity and protect your teeth against future damage. The frequency of treatments will depend on your individual needs and the severity of your sensitivity.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers can provide temporary relief from tooth sensitivity after whitening. Analgesics like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help to reduce the pain and discomfort. These medications work by blocking pain signals, allowing you to manage the sensitivity more comfortably. Always follow the recommended dosage instructions on the packaging to avoid any potential side effects. While these pain relievers can be very effective for managing acute pain, they are not a long-term solution. It is important to address the underlying cause of your tooth sensitivity through other treatments and lifestyle adjustments, such as using sensitive toothpaste, avoiding trigger foods, and practicing good oral hygiene. If your tooth sensitivity is severe or persistent, and pain relievers are not providing adequate relief, it is important to consult your dentist. They can evaluate your condition and recommend more effective strategies to manage the issue.
Soft Food Diet

Adopting a soft food diet can significantly reduce the discomfort associated with tooth sensitivity after whitening. Hard, crunchy, or chewy foods can irritate sensitive teeth, making the pain worse. A soft food diet involves consuming foods that require minimal chewing and do not put excessive pressure on the teeth. Examples include cooked vegetables, soups, yogurt, smoothies, and mashed potatoes. Avoid very hot or cold foods and drinks, as these can trigger sensitivity. It is important to chew on both sides of your mouth to distribute the pressure evenly. This dietary approach helps to minimize irritation and gives your teeth time to heal. As the sensitivity subsides, you can gradually reintroduce other foods back into your diet. Make sure you maintain a balanced diet, even while eating soft foods, to ensure you are getting all the necessary nutrients. If your sensitivity is severe, consult your dentist about the best foods to eat and what you should avoid to facilitate healing.
Professional Dental Treatments
In some cases, professional dental treatments may be necessary to effectively address tooth sensitivity after whitening. Your dentist can offer a variety of treatments that go beyond over-the-counter solutions. One common option is a fluoride varnish, which is applied directly to the teeth to strengthen the enamel and reduce sensitivity. Dentists may also apply desensitizing agents to the exposed dentin tubules, blocking the nerve signals that cause pain. If the sensitivity is caused by minor gum recession or other structural issues, your dentist might recommend dental bonding to cover exposed root surfaces. If the sensitivity is severe or persistent, a dentist may also recommend other treatments, such as a root canal, if necessary. Regular dental checkups are essential because they allow your dentist to monitor your teeth’s condition, identify potential issues early on, and offer the most appropriate treatment options. Always discuss your concerns with your dentist to develop the most effective treatment plan for your specific needs.
Essential Aftercare Tips for Whitening
Proper aftercare is crucial for minimizing tooth sensitivity after whitening and ensuring the longevity of your results. Begin by avoiding foods and beverages that can stain your teeth, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored berries, especially during the first few weeks after your treatment. Use a sensitive toothpaste twice a day, and consider using a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent further irritation. Avoid smoking, as it can stain your teeth and also contribute to sensitivity. Maintain a good oral hygiene routine, including flossing daily and rinsing with a non-alcoholic mouthwash. Schedule regular dental checkups to monitor your oral health and address any potential issues promptly. Follow the instructions provided by your dentist or the manufacturer of your whitening product carefully. Be patient; the sensitivity should gradually subside as your teeth recover. If the sensitivity persists or worsens, consult your dentist for further evaluation and treatment options. Following these aftercare tips will not only reduce your discomfort but also protect and preserve your bright, white smile.
Avoidance of Trigger Foods and Drinks
Avoiding trigger foods and drinks is a critical step in managing tooth sensitivity after whitening. Certain foods and beverages can exacerbate sensitivity by irritating the teeth or causing further enamel erosion. Generally, you should avoid extremely hot or cold items, like hot coffee, ice cream, or ice-cold water, as they can stimulate the nerves in your teeth and cause pain. Acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, vinegar, and carbonated beverages, can also erode enamel and increase sensitivity. Sugary foods and drinks are best avoided as they promote bacterial growth and can increase the risk of cavities. When you do consume foods and drinks, it is important to rinse your mouth with water afterward to minimize their effects. Consider making a list of foods and drinks that cause you sensitivity and gradually reintroduce them into your diet. By being mindful of your diet, you can greatly reduce your discomfort and allow your teeth to heal. Always consult your dentist if you have any concerns or need specific dietary recommendations.
Gentle Brushing Techniques
Using gentle brushing techniques is essential for managing tooth sensitivity after whitening. Aggressive brushing can further irritate the teeth and gums, leading to increased sensitivity. Instead of applying excessive pressure, brush your teeth using gentle, circular motions. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush, which is gentler on the enamel and gums than medium or hard-bristled brushes. Brush your teeth for at least two minutes, twice a day, ensuring you reach all surfaces of your teeth. Avoid brushing immediately after consuming acidic foods or drinks, as your enamel may be slightly softened, and brushing could cause further damage. Focus on using a gentle touch and not scrubbing vigorously. If you have receding gums, be extra careful to avoid brushing the exposed root surfaces, which are more sensitive. Consider using a timer or a toothbrush with a built-in timer to ensure you brush for the recommended amount of time. Proper brushing technique is an integral part of oral hygiene and can protect your teeth from various problems, including sensitivity.
Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are a key component of maintaining overall oral health and managing tooth sensitivity after whitening. During these checkups, your dentist can assess the condition of your teeth and gums, identify any potential problems, and offer personalized recommendations for your oral care. They can also provide professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup, helping to keep your teeth and gums healthy. Regular checkups allow your dentist to detect issues like cavities, gum disease, and enamel erosion early on, which can then be addressed before they cause significant sensitivity. The dentist can also apply fluoride treatments, which can strengthen the enamel and reduce sensitivity. They can offer specific advice on managing sensitivity, such as recommending the best toothpaste, avoiding trigger foods, and practicing proper brushing techniques. The frequency of dental checkups varies depending on your individual needs, but the general recommendation is to visit the dentist every six months. Making and keeping your dental appointments is critical for long-term oral health and can help prevent and manage tooth sensitivity.
When to Seek Professional Help
While tooth sensitivity after whitening is often temporary, there are times when you should seek professional help. If the sensitivity is severe, persistent, or worsens over time, it is important to consult your dentist. If the pain is interfering with your ability to eat, drink, or perform daily activities, professional intervention is warranted. Moreover, if you experience other symptoms, such as bleeding gums, swelling, or any signs of infection, it is essential to seek immediate dental care. Your dentist can assess your condition, rule out any underlying dental issues, and recommend appropriate treatments. They may suggest specific desensitizing agents, fluoride treatments, or other interventions. If you have pre-existing dental conditions, such as gum disease, cavities, or enamel erosion, it’s crucial to discuss them with your dentist before undergoing teeth whitening. In some cases, whitening may not be recommended, or it might need to be postponed until these issues are addressed. Always rely on your dentist for personalized advice and treatment to ensure your oral health.
